The brain and spinal cord interact a lot with our endocannabinoid system (ECS). Supporting this interaction may hold the key to promoting long-term cognitive and mental health. Let’s learn about the potential neurological benefits of phytocannabinoids like CBD to support a healthy ECS-brain relationship.
What are the potential neurological benefits of phytocannabinoids?
The primary function of our ECS is to maintain homeostasis. Homeostasis prevents our body systems from being too under- or overactive.
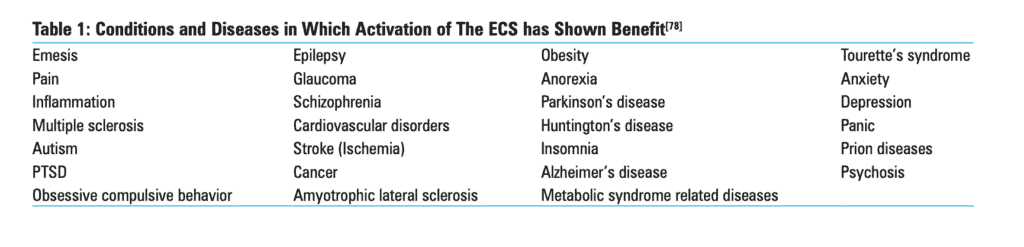
In 2018, researchers conducted a thorough review of all the scientific research that focused on the relationship between our central nervous system and ECS. Table 1 below shows conditions and diseases identified by the researchers that are related to our nervous system and benefit from healthy ECS activity:
The researchers discussed how all of the conditions above are exacerbated by either too much or not enough activity in certain parts of the body, especially the brain. Therefore, the researchers hypothesize that, by supporting homeostasis through our ECS, we can help our body maintain long-term health, both in our nervous system and more broadly.
ECS activity in the brain
The central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, may have the most ECS activity of anywhere in the body. Researchers have identified many functions of the ECS in the brain which play vital roles in maintaining neurological health.
CB1 receptors are the primary ECS receptors in the central nervous. These receptors influence cognitive function, memory, pain perception, focus, and more. As described above, they can help reduce hyperactivity or increase low activity. Essentially, ECS receptors help stabilize nervous system activity.
For example, CB1 receptors in the brain are shown to be very useful in regulating neurotransmitter activity, which can reduce the risk of seizures. This is why CBD has been so widely studied for helping those prone to seizures.
Another example is how the ECS may play a significant role in addiction. Dopamine is the primary neurotransmitter implicated in addictive behaviors, from over-eating (which can lead to obesity and diabetes) to drug addiction. Normalizing dopamine levels is very important for helping those who suffer from addiction, and our ECS may help normalize dopamine activity.
How phytocannabinoids interact with our brain
THC can easily bind with CB1 receptors. This is what gives THC its intoxicating effect. But THC doesn’t bind to CB1 receptors with any rhyme or reason, it simply binds to all it comes in contact with. As a result, this can cause anxiousness, paranoia, and other adverse effects that make for an unpleasant experience.
On the other hand, CBD itself does not readily bind to ECS receptors. Instead, it supports our body’s own endocannabinoids – AEA and 2-AG – by maintaining a healthy supply in circulation. Then, our ECS itself sends those signals to CB1 receptors when appropriate.
Of course, THC can be beneficial in small amounts, and especially when combined with CBD. That’s because CBD actually helps moderate and temper the activity of THC.
Additionally, researchers believe that CBD may help reduce inflammation in the brain. Inflammation is recognized as a key pathway to developing many diseases around the body. In the brain, inflammation may lead to the accumulation of beta-amyloid plaques. Researchers believe these plaques may cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Therefore, the researchers conclude that CBD’s ability to reduce neuroinflammation may be helpful in preventing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
Another literature review from early 2020 showed how CBD also shows promise in helping with behaviors associated with psychosis, anxiety, and PTSD. CBD has also shown an ability to reduce the impact of brain damage associated with neurodegenerative and ischemic (stroke) conditions.
Of course, more research is needed to expand and confirm all of these preliminary findings.
Support a healthy ECS for neurological health
The interactions between our ECS and nervous system are well-established, with a lot of CB1 receptors found especially in the brain and spinal cord. These receptors influence a lot of nervous system activity, including that of neurotransmitters which are associated with conditions from addiction to seizures. Additionally, this research is finding that, when normal, these ECS receptors play an important role in avoiding the progression of certain conditions.
Researchers are theorizing that, by supporting the function of our ECS in maintaining homeostasis, we may help combat the progression of many common and deadly neurological disorders. Additionally, researchers are optimistic that this link will become more clear with more studies. Indeed, the ECS may present an exciting new focus to maintain nervous system health, with the neurological benefits of phytocannabinoids as a new treatment method.
References:
Maroon J, Bost J. Review of the neurological benefits of phytocannabinoids. Surg Neurol Int. 2018;9(1):91.
Burstein S. Cannabidiol (Cbd) and its analogs: a review of their effects on inflammation. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 2015;23(7):1377-1385.
Chadwick VL, Rohleder C, Koethe D, Leweke FM. Cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system in anxiety, depression, and dysregulation of emotion in humans. Current Opinion in Psychiatry. 2020;33(1):20-42.
Interested in other new research regarding our endocannabinoid system? Check out this recent article on Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency.